We handle the transaction of tasks within implementation projects in the course of our development, implementation work.
In the course of choosing the applied developmental methodology during the projects, we equally undertake to complete the developmental tasks with taking account of the facilities and demands of the customer with the application of: classic waterfall model or SCRUM methodolgy.
The following main activities are the part of the developmental process independently of the methodology applied during the implementation:
- Requirement analysis and specification our business analyst colleagues interpret the emerging needs and they formalise the implementation plan for the user in an understandable way
- As far as possible making of formalised, reusable, specific documents
- Persistant functional testing from the beginning of development, which concentrates not only on meeting the requirements, but it regards the birth of the usable solution as an important task
- Making draft versions and presentation of them as far as possible
- Development with tool support, which extends to the following:
- Strict version handling
- Automatic build solutions
- Automatic business-logic testing
- Designing and tracking of development tasks
- Handling of documentations and knowledge
- Test design, description of test cases, tracking of testing process
- Bug and fix tracking
- Release management
Classic ’waterfall’ model
It is a lineal step-sequence, which breaks up the development of the applications into separated and being implemented one after the other phases. Every phase is implemented only once during the development, this model does not plan a backward step (does not plan taking a step backward) to modify the previous developmental phases.
The borders of the phases are determined according to the existence of the recommendation and particular documentations (representations) as well as the summary and appraising discussion has to be held, which helps to review these documentations.
Necessary outputs, which start up during the tasks:
- requirement-specification
- plans
- checked code (meet the requirements)
- integration achievements
Principles applied in the course of using the waterfall model:
- The objectives can be reached in the easiest way with the application of the well-defined and documented milestones. These milestones split the development into well-defined sequential phases.
- The role and lucidity of the documents are significant.
- Every detail of the requirements and wanted functions are known before the start of development and these do not change during the development.
- Testing and appraisal can be carried out only at the end of the development
SCRUM
The srcum is a framework, which includes certain activities and defined roles. The main cues of the SCRUM are: the ’SCRUM Master’, who supervises the process and their work is similar to the project manager’s, the ’Product Owner’, who stands for the decision-makers, who are concerned in the project, and the ’Team’, which members cover the all work items.
During every sprint - which means duration between 2 and 4 weeks (depending on the Team’s decision) - the Team creates an operating software unit. Functions, which should be implemented during the sprint are from the ’Product Backlog’ (to-do-list of the product), which is a list of the requests on high level related to the work in order of importance. There is a ’sprint-planner’ discussion at the beginning of the sprint, where the Team decides which elements of the list will be implemented in the course of the sprint. During the talk the ’Product Owner’ tells the team which ones from the to-do-list should be done the soonest. After that the team decides which ones from these can be implemented during the next sprint and make a promise to work it out. The to-do-list (of the sprint) can not be altered during the sprint, the completed operations are fixed. As soon as the sprint has terminated, the team shows the complete functions (demo).
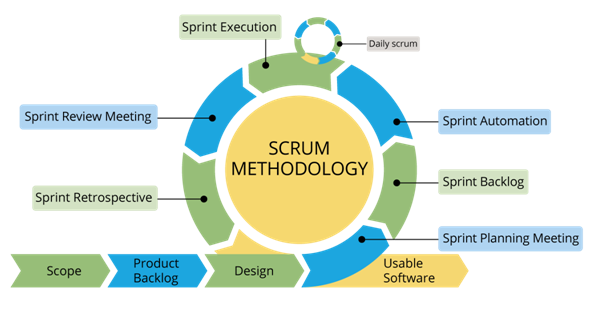
The SCRUM motivates the participants of the project to work at the same place and to communicate verbally to each other.
One of the most important principles of the SCRUM is to recognise and accept that the clients might change their minds in connection with the requirements during the development, and the unexpected changes can not be handled easily with the traditional solutions based on previous developmental phase. Therefore the SCRUM chooses practical approach and accepts there is no possibility to understand and define the problem entirely. It rather tries to help the team to be able to implement the functions and to react to the changing requirements quickly.



